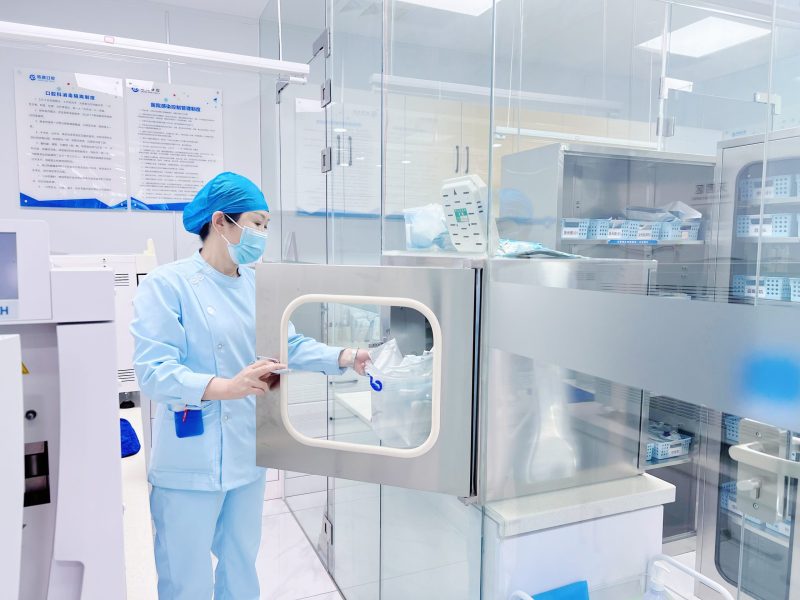
The disinfection of dental instruments is an essential part of healthcare. While the importance of sterilization may seem self-evident, it is an absolutely critical step that cannot be overlooked. In the field of dental care, healthcare professionals commonly use methods such as steam, dry heat, or unsaturated chemical vapor for instrument sterilization. This process aims to thoroughly eliminate bacteria and other active microorganisms on the instruments, which is vital for ensuring the safety of both patients and dental professionals.
By disinfecting dental instruments, the transmission of bacteria and pathogens can be effectively prevented. In other words, this process ensures that dental professionals do not inadvertently spread viral or bacterial infections to patients due to instrument issues during treatment. Therefore, adhering to proper sterilization procedures is a key safeguard for maintaining patient health.
In dental clinics, the correct sterilization methods not only concern patient safety but also the self-protection of dental professionals. It effectively prevents the growth of bacteria on instruments and clinic surfaces, thereby stopping the spread of bacteria between individuals.

How Are Dental Instruments Sterilized?
The disinfection of dental instruments is a complex and stringent process that requires adherence to professional protocols and standards. By following proper disinfection procedures, the cleanliness and sterility of dental instruments can be ensured, safeguarding both patient and dental professional safety. The main steps include:
1. Pre-Cleaning
Using running water or a cleaning machine, dental instruments undergo an initial rinse to remove surface contaminants and residues. This step is foundational for subsequent disinfection and sterilization, helping to ensure effective results.
2. Deep Cleaning
For complex dental instruments, such as turbines and root canal files, ultrasonic cleaners are employed for thorough cleaning. Ultrasonic cleaning utilizes high-frequency vibrations to remove tiny dirt and bacteria from the instrument’s interior.
3. Disinfection Treatment
Disinfection is a critical stage in the sterilization process. Depending on the material and heat resistance of the instruments, different disinfection methods can be selected:
- High-Temperature, High-Pressure Steam Sterilization: For heat-resistant dental instruments, such as metal extraction forceps and dental trays, this method effectively kills all microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and spores. Sterilized instruments should achieve a sterile state, making them safe for patient treatment.
- Chemical Disinfection: For heat-sensitive instruments, such as precision implants and blades, chemical disinfection methods are used. Common disinfectants include chlorine-based solutions and glutaraldehyde. These agents disrupt microbial cell structures to achieve disinfection. It is essential to follow the instructions carefully to avoid excessive soaking times or concentrations that may cause corrosion or damage to the instruments.
4. Drying Treatment
After disinfection, dental instruments must be dried to remove any residual moisture and disinfectants. Drying can be performed using drying equipment or cloths, ensuring that both the surfaces and interiors of the instruments are completely dry to prevent bacterial growth.
5. Storage and Labeling
Sterilized dental instruments should be stored in a clean, dry, and light-protected environment, with labels indicating the disinfection date and validity. Storage containers should be regularly cleaned and disinfected to avoid contamination. Additionally, it is crucial to keep the storage area isolated from contaminants to maintain cleanliness and hygiene.
6. Precautions
Throughout the disinfection process, personnel should wear appropriate protective gear, such as gloves and masks, to avoid contact with contaminants and irritation from disinfectants.
Disinfectants should be prepared fresh for immediate use to prevent potency loss or failure from prolonged storage.
For single-use dental instruments, such as syringes and mouth mirrors, they should be discarded immediately after use and disposed of according to medical waste regulations.
Which disinfection step is the most important?
In the disinfection process of dental instruments, while each step is crucial, high-temperature steam sterilization and chemical disinfection methods are typically considered the most critical stages.
High-Temperature Steam Sterilization is one of the most effective disinfection methods, capable of thoroughly killing all microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and spores, ensuring that instruments reach a sterile state. The importance of this step lies in providing the highest level of disinfection assurance, thereby minimizing the risk of cross-contamination.
Chemical Disinfection is a necessary choice for instruments that are heat-sensitive. Appropriate disinfectants can disrupt the cell structure of microorganisms, achieving disinfection objectives. While its efficacy may be slightly lower than steam sterilization, it remains a safe and effective method in cases where material limitations apply.
Regardless of the chosen disinfection method, it must be performed under appropriate conditions, including correct disinfectant concentration, temperature, time, and pH levels. Post-disinfection drying and storage management are also vital to ensure that instruments remain sterile over time.
In summary, although each step has a unique role, high-temperature steam sterilization and chemical disinfection methods are often seen as key steps because they directly determine the disinfection effectiveness of the instruments. Meanwhile, the other steps should not be overlooked, as they collectively form a complete system to ensure the safety and hygiene of dental instruments.
How Long to Sterilize Dental Equipment?
The time required for disinfecting dental equipment depends on various factors, including the type of equipment, material, size, and the disinfection method used. Here’s a detailed analysis of the disinfection times for dental equipment:
1. High-Temperature, High-Pressure Steam Sterilization
- Standard Disinfection Time: Dental autoclaves are typically used for high-temperature, high-pressure steam sterilization of dental instruments. In regular operations, the disinfection time is usually set between 20 to 30 minutes. This timeframe considers the performance of the equipment, as well as the size and type of the items being disinfected.
- Special Instrument Disinfection Time: For certain specialized instruments, such as periodontal treatment tips that are more delicate, the disinfection time may need to be adjusted. These instruments are susceptible to damage in high-temperature, high-pressure environments, so it is recommended to use lower temperatures or shorten the disinfection time. However, specific procedures should follow the device manuals and professional standards.
2. Chemical Disinfection Method
- Disinfection Time: The disinfection time for chemical methods typically depends on the type of disinfectant used, its concentration, and the degree of contamination of the instruments. Different disinfectants have varying disinfection time requirements, so strict adherence to the instructions is necessary.
- Precautions: Chemical disinfectants should be prepared fresh for each use to prevent reduced efficacy from prolonged storage. Excessively high concentrations or extended soaking times may lead to corrosion or damage to the instruments, so it’s crucial to control the disinfection time and concentration strictly.
3. Other Disinfection Methods
In addition to high-temperature, high-pressure steam sterilization and chemical methods, other disinfection techniques, such as ultraviolet (UV) disinfection and ozone disinfection, can also be used for dental equipment. The disinfection times for these methods vary based on the type of equipment, the disinfectant used, and operational protocols.
In summary, the time required for disinfecting dental equipment varies based on the type, material, size, and disinfection method. To ensure effective disinfection, it is essential to follow professional guidelines and refer to the equipment manuals. Regular maintenance and servicing of disinfection equipment are also key to ensuring optimal disinfection outcomes.
Conclusion
Dental instrument sterilization is a crucial step in healthcare, ensuring the safety of patients and dental professionals. It involves several steps, including pre-cleaning, deep cleaning, disinfection treatment, drying treatment, storage and labeling, and precautions. High-temperature steam sterilization and chemical disinfection methods are considered the most critical stages, as they directly determine the disinfection effectiveness of the instruments.