Dental implants, as a popular and effective method for replacing missing teeth, provide many patients with a lasting and reliable solution. However, despite their high success rate, dental implants can sometimes encounter failure or fracture. For dental professionals and patients alike, understanding the causes of dental implant fractures and taking appropriate preventive measures are crucial for ensuring the long-term efficacy and success rate of implants. This article aims to explore the factors leading to dental implant failures, effective prevention strategies, and the key role of ongoing care and maintenance in ensuring the success of dental implants.
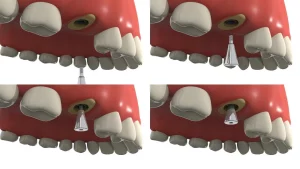
Reasons Why Dental Implants Break
Overload Issues
One significant cause of dental implant fractures is the overload, which occurs when the implant endures forces exceeding its design limits. This often happens when patients attempt to chew extremely hard foods with their implants. Over time, this excessive force can lead to small displacements of the implant within the bone, potentially resulting in loosening or even fracture.
Insufficient Jawbone Volume
The success of dental implants relies on their close integration with the jawbone. However, insufficient bone density, improper implant placement, or certain health conditions that affect bone healing (such as diabetes or osteoporosis) can lead to poor osseointegration. Without adequate bone support, implants are more prone to fracture. If implants are placed in shallow bone areas, they become vulnerable and susceptible to breakage. Therefore, accurately planning the implant position through 3D CT scans prior to surgery is crucial to ensure maximum support. For patients with insufficient bone volume, dental professionals may recommend bone grafting procedures before implant placement.
Improper Selection or Placement of Implants
The success of dental implants also depends on the precise selection and placement by the dentist. The size, type, and position of the implants in the patient’s bone must be accurately matched to the bone density and bite force. Incorrect selection or placement can lead to excessive pressure on the implants, increasing the risk of failure. When the position of the missing teeth is poor, they may exert additional pressure on the implants, making them weak and prone to fracture over time.
Peri-implantitis
Peri-implantitis is an inflammatory process that affects the tissues surrounding the implant, leading to the loss of supporting bone. This condition is often caused by bacterial infections resulting from poor oral hygiene. As the supporting bone deteriorates, the stability of the implant is compromised, increasing the risk of failure.
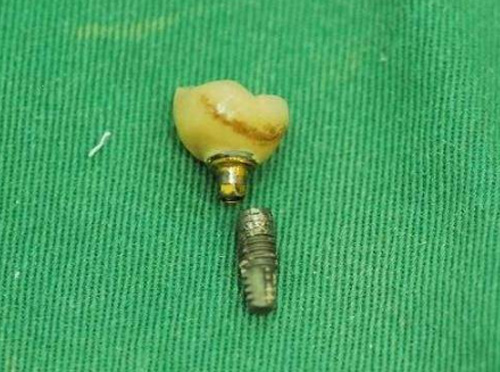
Low-Quality Implant Fixtures
Choosing inexpensive implant fixtures may save costs for dentists but can pose significant risks. Some manufacturers produce implants at extremely low prices, but their quality is questionable. In contrast, DentalMaster implants use high-grade grade 4 cold-work titanium, combining quality materials with precision design and excellent SLA surface treatment to enhance bone compatibility. Using low-quality fixtures can lead to implant damage. Therefore, selecting high-quality dental implant fixtures is essential.
Measures to prevent dental implant damage
- Proper Planning and Assessment
Comprehensive Examination: Before deciding to undergo dental implant surgery, patients should have a thorough oral health check, including the condition of teeth, gum health, bone density, and oral structure.
Lifestyle Assessment: Patients’ dietary habits, smoking habits, and oral hygiene practices can affect the success rate of dental implants. Therefore, doctors need to understand patients’ lifestyles in detail and provide corresponding advice.
Selecting the Right Implant: Based on the patient’s specific situation, doctors should choose the most suitable type, size, and placement of the implant to ensure optimal stability and long-term results. - Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
Regular Brushing: Brush at least twice a day using a soft-bristle toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste, gently cleaning the implant and surrounding gums.
Use Dental Floss: Dental floss helps remove food debris and plaque between teeth, preventing interproximal cavities and periodontal disease.
Professional Cleaning: Regular visits to the dental clinic for professional teeth cleaning and check-ups can remove tartar and plaque that are difficult to clean on your own. - Avoid Hard and Sticky Foods
Hard Foods: Foods such as nuts, hard candies, and bones may exert excessive pressure on the implants, leading to loosening or damage.
Sticky Foods: Foods like chewing gum and caramel can easily stick to the implants, making them difficult to clean and increasing the risk of periodontal disease. - Regular Dental Check-Ups
Routine Exams: Have a comprehensive oral examination at least once a year, including the stability of the implants, gum health, and occlusion relationships.
X-ray Checks: Regular X-rays should be taken to monitor bone density and changes around the implants. - Use Mouthguards
Bruxism Patients: For those who grind their teeth at night, wearing a mouthguard can reduce wear and damage to the implants.
Contact Sports: When participating in contact sports like football or basketball, wearing a mouthguard can protect teeth and implants from accidental impacts. - Other Considerations
Avoid Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of implant failure, as harmful substances in tobacco can damage gum and bone health.
Balanced Diet: Maintaining a balanced diet with adequate calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D is essential for bone health.
Avoid Excessive Force: When using dental floss or a toothbrush, avoid excessive force to prevent damaging gums and soft tissue around the implants.
In summary, through proper planning and assessment, maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding hard and sticky foods, regular dental check-ups, using mouthguards, and paying attention to other relevant matters, patients can significantly reduce the risk of implant damage and enjoy the convenience and aesthetics of dental implants in the long term.
Importance of Ongoing Care for Dental Implants
- Preventing Oral Diseases
Dental implants can easily accumulate food debris and bacteria, leading to gum irritation, inflammation, and conditions like gum recession and periodontal disease. Regular oral care, including brushing, flossing, using mouthwash, and professional cleanings, helps eliminate these deposits and reduces bacterial growth, effectively preventing oral diseases. - Maintaining Implant Stability
The stability of dental implants is essential for their functionality. Through regular maintenance, dentists can assess the implant’s stability and bone condition, identifying potential issues like loosening, infection, or bone loss. Timely intervention is crucial, as unresolved problems can lead to implant failure, making ongoing care vital for implant stability. - Extending Implant Lifespan
While dental implants are a reliable tooth replacement solution, their longevity depends on patient care. Regular maintenance reduces the risk of infection and inflammation, keeping the mouth clean and minimizing bacterial growth, which helps prolong the implant’s lifespan. Additionally, timely care can identify and address surrounding issues, preventing further damage. - Enhancing Oral Health and Quality of Life
Dental implants restore chewing function and aesthetics, boosting patients’ confidence and quality of life. However, neglecting their care can lead to frequent oral problems that affect daily life and overall health. Continuous care is essential for maintaining the health of implants and enhancing overall oral health and quality of life. - Avoiding Unnecessary Medical Expenses
Poor maintenance of dental implants can result in loosening, infection, or other complications requiring surgical intervention or re-implantation. Such treatments not only increase financial burdens but also cause additional discomfort. Ongoing care can prevent unnecessary medical costs and surgical risks, ensuring both financial and physical well-being.