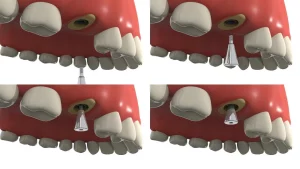
The Locator Abutment is a connection component used in dental implant restoration, primarily functioning to connect the implant to the prosthetic restoration (such as dentures). It provides a stable foundation, ensuring accurate positioning and a good fit of the restoration. The design of the Locator abutment typically features a unique shape and height, allowing dentists to make precise adjustments and positioning in the oral cavity. Additionally, it helps achieve ideal aesthetic results and functionality, enhancing patient comfort and satisfaction. This article will explore the definition of the Locator abutment, the key factors in selecting its height, and how to remove the Locator abutment.
Functions of Locator Abutments in Dentistry
Locator abutments serve multiple important functions in the field of dentistry, crucial for ensuring surgical precision, improving restoration accuracy, simplifying the surgical process, and enhancing patient satisfaction. Here are the main functions of locator abutments:
- Precise Positioning: Locator abutments provide a stable and precise three-dimensional reference point, helping dentists accurately determine the position and angle of implants during surgery. When combined with digital technologies (such as CBCT scans and 3D-printed guides), locator abutments can further enhance surgical accuracy.
- Guiding Implantation: Locator abutments are typically designed to match the shape and size of the implant, acting as a guiding tool to ensure the implant is correctly placed in the intended position. This helps avoid misplacement or angular deviations of the implant, ensuring its stability and long-term success.
- Simplifying the Surgical Process: Using locator abutments can simplify the surgical process, reducing surgery time and lowering risks. Dentists can perform procedures with greater confidence, as locator abutments provide additional support and guidance.
- Improving Restoration Accuracy: During the restoration phase, locator abutments assist dentists in precisely installing and adjusting prosthetic devices (such as crowns or bridges) to ensure a perfect fit with surrounding teeth and tissues. This contributes to the aesthetic, functional, and comfort aspects of the restoration.
- Supporting Long-term Maintenance: Locator abutments can also serve as maintenance tools, aiding dentists in easily locating the implants and restorations during follow-up check-ups and maintenance. This facilitates the timely identification and management of any potential issues, extending the lifespan of the implant.
- Enhancing Patient Satisfaction: By providing precise, stable, and reliable implant and restoration outcomes, locator abutments help improve patient satisfaction and trust. Patients can confidently showcase their smiles and enjoy better oral health and quality of life.
How to Choose the Height of Locator Abutments
In dental implant therapy, selecting the appropriate height of the locator abutment is crucial. The height of the abutment directly affects the function, aesthetics, and comfort of the restoration.
Individualized Treatment Plans
Every patient’s situation is unique, so an individualized treatment plan should be adopted when selecting abutment height. Based on the specific circumstances of the patient and considering the factors mentioned above, the most suitable abutment height selection plan can be developed to ensure the success of the treatment.
Patient’s Oral Anatomy
When choosing abutment height, the patient’s oral anatomy must first be considered. The height and shape of the alveolar bone are critical factors. By obtaining accurate data through imaging examinations (such as CBCT), dentists can better assess the bone condition and select an appropriate abutment height. For patients with insufficient alveolar bone height, a shorter abutment may be necessary to avoid conflicts with opposing teeth or other structures.
Tooth Function and Occlusion
The height of the locator abutment must also consider the patient’s occlusal relationship and tooth function. The restoration needs to coordinate with opposing teeth to ensure normal occlusal function and comfort. Dentists should choose the appropriate abutment height based on the patient’s occlusal situation to avoid discomfort and functional issues caused by abutments that are too high or too low.
Soft Tissue Thickness and Height
The thickness and height of the soft tissue are important considerations in selecting abutment height. The morphology of the soft tissue can impact the aesthetics and healing process of the restoration. Generally, the abutment height should match the surrounding soft tissue height to achieve good aesthetics and function. Dentists can determine the best choice for abutment height by assessing the soft tissue.
Implant Type and Design
Different types of implants may have varying requirements for abutment height. Dentists need to understand the specific design of the implant being used and the recommended abutment type. Ensuring compatibility between the selected abutment and the implant can help increase the success rate of the treatment.
Type of Restoration
The type of restoration also directly influences the choice of abutment height. Full crowns, partial crowns, and other types of restorations have different design and functional requirements. Choosing the appropriate abutment height ensures the stability and aesthetics of the restoration.
Clinical Experience and Literature Reference
The dentist’s clinical experience and relevant literature references are also essential. By analyzing previous cases, dentists can summarize best practices and provide better recommendations for new patients. Additionally, staying updated with the latest research and technological developments in the field enhances the dentist’s expertise and treatment outcomes.
Applications of Locator Abutments
Locator abutments are widely used in dental implant restorations, especially when stability and aesthetics are required. Here are their main application areas:
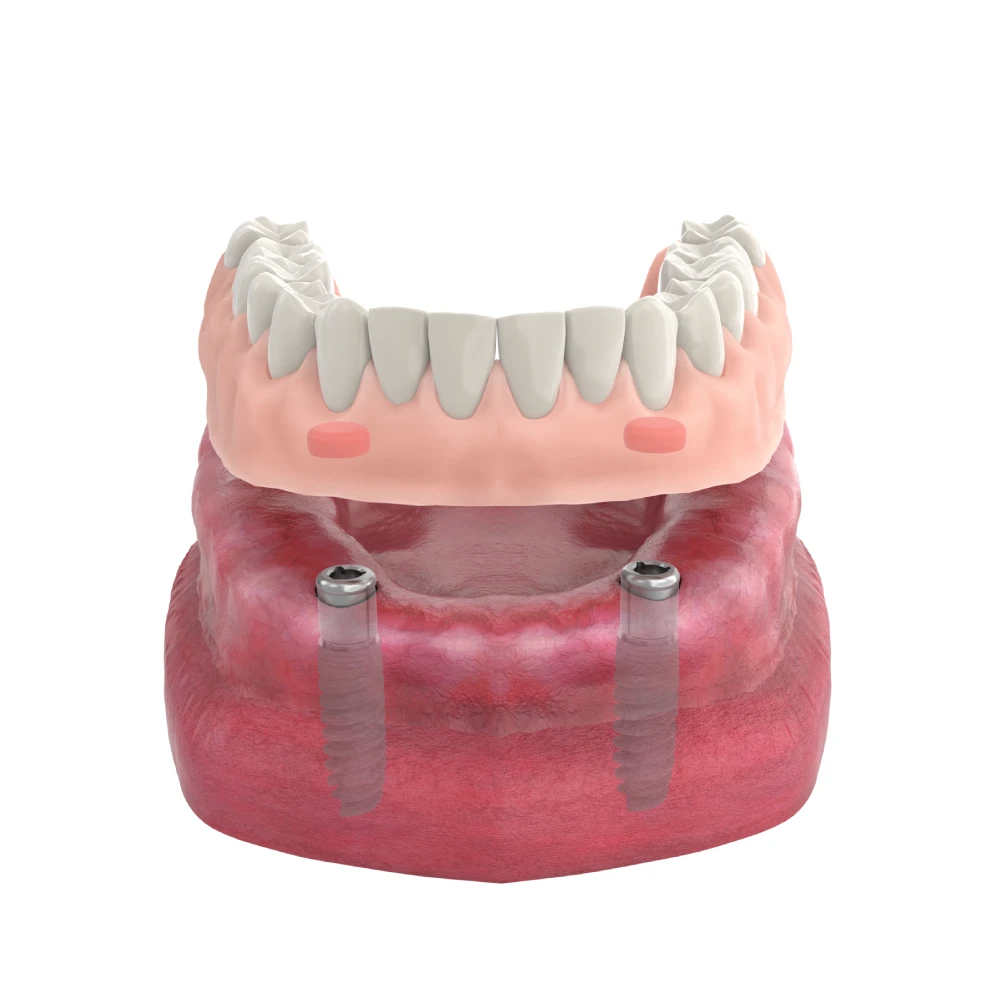
- Denture Restoration
Locator abutments are commonly used to support removable dentures, providing a stable connection that keeps the dentures more securely in the mouth. This design enhances the patient’s chewing function and comfort while reducing movement and dislodgment of the dentures. - Fixed Restorations
In fixed restorations, locator abutments serve as the connecting component between the implant and the crown or bridge, ensuring good fit and function. Their design helps improve the stability of the restoration, ensuring long-term success. - Precise Positioning
Locator abutments provide reliable reference points, assisting dentists in accurately placing implants during surgery. This is particularly important for complex implant procedures, effectively reducing surgical risks and complications. - Aesthetic Results
In aesthetic restorations, locator abutments can coordinate with the shape and height of surrounding soft tissues to achieve a natural appearance. Good soft tissue healing can also boost the patient’s confidence. - Simplified Maintenance
The simple design of locator abutments facilitates easy maintenance and adjustments. Dentists can quickly locate and check the implants and restorations, addressing any potential issues in a timely manner to extend the lifespan of the restoration. - customisedIndividualized Treatment
The diverse designs of locator abutments allow for meeting the personalized needs of different patients. Dentists can choose the appropriate abutment based on the specific circumstances of each patient, providing customized treatment plans.
How to remove locator abutments
Removal of locator abutments is a dental procedure that requires professional knowledge and skills and should be performed by an experienced dentist. Here’s an overview of the basic steps involved:
- Local Anesthesia
Administer local anesthesia around the abutment to reduce the patient’s pain and discomfort. - Remove Coverings
Carefully use dental tools, such as pliers or screwdrivers, to remove any fillers, debris, or healing caps around the abutment. - Loosen the Abutment
Gently tap or pry the surrounding alveolar bone with appropriate tools to help loosen the abutment. This step must be done cautiously to avoid damaging surrounding tissues and structures. - Extract the Locator Abutment
Once the abutment is sufficiently loose, the dentist will use tools (like a wrench or screwdriver) to gently rotate and pry the abutment, completely removing it from the alveolar bone. - Clean and Repair
After removal, thoroughly clean the alveolar bone and surrounding soft tissue. This usually involves rinsing with saline or antiseptic solutions and removing any residual debris or fragments. The dentist may also perform additional repair work, such as smoothing the bone surface or addressing any damaged tissues. - Post-Operative Care
Patients need to follow the dentist’s post-operative care instructions after the removal. This may include avoiding irritating foods, maintaining oral hygiene, and taking antibiotics to prevent infection. The dentist may also recommend avoiding strenuous activities that could impact oral recovery. - Evaluate Further Treatment
After removing the abutment, the dentist will assess the patient’s oral condition and determine if further treatment or repairs are needed. If reinstallation of the abutment or other restorative work is necessary, the dentist will develop an appropriate plan and schedule follow-up treatments.
Please note that these steps may vary based on the patient’s specific situation and the dentist’s practices. Removing locator abutments is a complex procedure that should be carried out by an experienced dentist in a suitable medical facility. If you need to have a locator abutment removed, be sure to consult a professional dentist and follow their guidance.
Conclusie
De Locatieabutment is a crucial component in dental implant restoration, connecting the implant to prosthetic restorations. It provides a stable foundation, ensuring accurate positioning and a good fit. The design of the abutment, typically with a unique shape and height, allows dentists to make precise adjustments and positioning in the oral cavity. It also enhances aesthetic results and functionality, enhancing patient satisfaction. The height of the locator abutment is crucial, and an individualized treatment plan should be adopted based on the patient’s oral anatomy, tooth function, and soft tissue thickness.