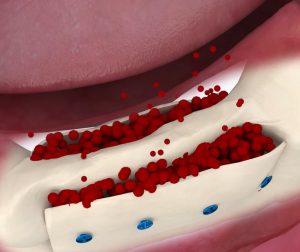
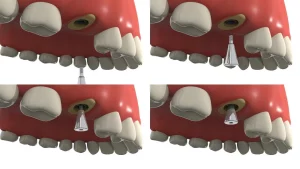
Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR) is a key technique in modern dentistry, particularly in dental implantology and periodontal treatment. It is a surgical procedure designed to regenerate lost or defective bone tissue by promoting the growth of new bone in areas of bone loss. This process ensures successful dental implant placement or the restoration of bone structure to support teeth affected by periodontal disease. GBR is especially important for patients with insufficient jawbone density to support implants, as well as for cases where bone volume has decreased due to periodontal disease, trauma, or long-term tooth loss. In this article, we will delve into the concept of GBR, how it works, and its benefits in dental treatment.
Understanding Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR)
Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR) is an advanced dental technique that strategically uses barrier membranes to direct the orderly growth of new bone in areas of bone defects. This technology brings hope to patients who have experienced bone loss due to trauma, infection, tooth extraction, or prolonged periodontal disease. When bone volume is insufficient, it not only affects the stability and success rate of dental implants but also poses a threat to the health of natural teeth.
The core principle of GBR lies in isolating the bone defect area from the surrounding soft tissues, thus creating a favorable microenvironment for bone regeneration. In this carefully isolated space, bone can grow freely without external interference, allowing its natural growth and healing ability to flourish. In this way, GBR ensures the formation of sufficient volume and density of new bone in the defect area, providing a solid foundation for the subsequent implantation of dental implants or the support of natural teeth.
How Does GBR Work?
Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR) typically follows these steps:
- Preparation Phase: The dentist will thoroughly clean the area around the bone defect using specialized titanium brushes to remove any inflamed or infected tissue, creating an ideal environment for bone regeneration.
- Bone Graft Placement: Carefully selected bone graft material—possibly sourced from the patient’s own body, a donor, or synthetic origin—is precisely placed in the area where bone regeneration is needed, serving as a solid scaffold for new bone growth. In this step, auxiliary tools such as membrane pins, bone screws, or tenting screws may be used to ensure the stability and accuracy of the bone graft material.
- Application of a Barrier Membrane: A biocompatible membrane is gently placed over the bone graft material. This membrane plays a crucial role in preventing fast-growing soft tissue, such as gum tissue, from invading the bone regeneration area, providing a protected space for new bone growth.
- Healing Process: The biocompatible membrane will remain in place for several months, during which time the body’s natural healing mechanism will promote new bone formation. Once the bone has regenerated to the desired state, the membrane will either be absorbed naturally or removed by the doctor. At this point, the deficient area will have sufficient bone volume and density to support dental implants or other restorative treatments.
Why is bone regeneration important?
Bone regeneration plays a critical role in dental treatments, especially in dental implant procedures. For successful implant placement, there must be enough healthy and high-quality bone to provide stable support. The integrity of the bone directly affects the success rate and long-term stability of the implant. Without sufficient bone, the implant may not secure properly, leading to a higher risk of failure. This could result in impaired chewing function and aesthetic complications, such as excessive gaps between teeth or facial contour collapse.
Moreover, the loss of the jawbone not only jeopardizes implant success but also significantly alters facial structure, making a person appear older and more fatigued. It also affects overall oral health. When jawbone volume decreases, the stability of teeth is compromised, increasing the likelihood of loose or lost teeth. This impacts chewing efficiency, speech clarity, and the natural self-cleaning mechanisms of the mouth.
This is where Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR) becomes essential. By promoting the growth of bone in deficient areas, GBR helps restore the necessary bone structure, providing a stable and healthy environment for implant placement. This technique not only increases the chances of successful implant surgery but also improves the patient’s facial aesthetics and oral health, restoring normal chewing function and overall quality of life.
Types of Membranes Used in Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR)
In Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR) technology, the types of membranes used can be broadly categorized into two main types:
1. Absorbable Membranes
Characteristics:
These membranes are made from natural materials (such as collagen) that can be naturally absorbed by the body. They gradually dissolve over time, eliminating the need for a second surgery to remove them.
Advantages:
- Reduced Surgical Burden: Avoids the pain and additional costs associated with a second surgery.
- Lower Infection Risk: Reduces the risk of postoperative infections.
- Enhanced Healing: Their hydrophilic properties, good biocompatibility, and quick tissue integration facilitate easy handling and promote healing.
Applications:
Typically suitable for mild to moderate bone defects, especially in cases where reducing the surgical burden on the patient is a priority.
2. Non-Absorbable Membranes
Characteristics:
These membranes are usually made from inert materials (such as polytetrafluoroethylene) or metals (like pure titanium), offering high durability and stability. They require a second surgery for removal after complete bone regeneration.
Advantages:
- Long-Term Stability: They provide strong support for the bone defect area over an extended period.
- Facilitates Extensive Bone Growth: Suitable for cases requiring more significant bone regeneration or in complex defect scenarios.
Applications:
Commonly used for severe horizontal or vertical bone defects and situations that require long-term stability and support.
Benefits of Guided Bone Regeneration
- Restoration of Jawbone Structure:
GBR technology aids in regenerating bone tissue, helping to rebuild lost bone due to periodontal disease, trauma, or other causes, thus restoring the natural shape and function of the jawbone. - Supporting Implants:
By increasing bone volume, GBR ensures sufficient bone quality to stabilize dental implants, enhancing the success rate of implant surgeries and making the implants more durable. - Prevention of Further Bone Loss:
By promoting the regeneration and repair of bone tissue, GBR helps prevent future bone resorption and loss, maintaining oral health and aesthetics.
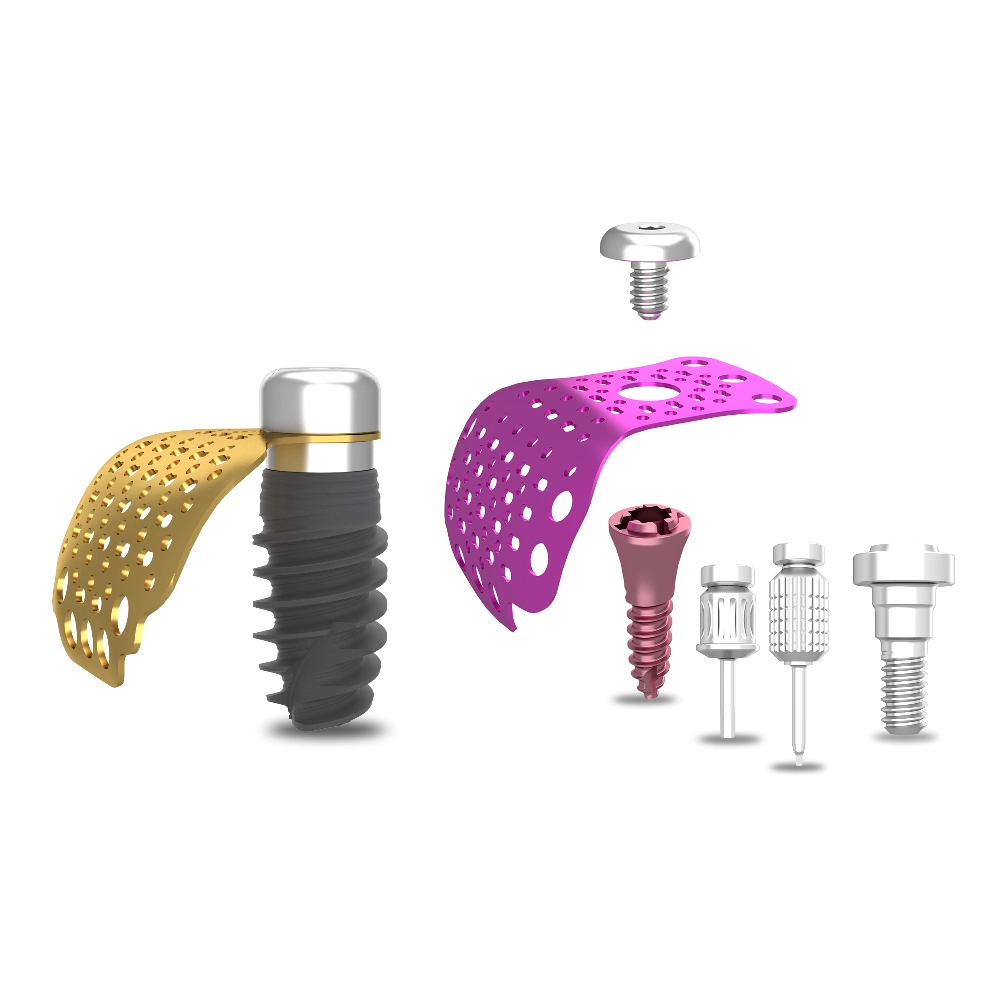
Membrane Tacks and Bone Screws Used in GBR
In Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR) technology, the use of membrane tacks and bone screws is crucial for securing the barrier membrane and ensuring the stability of the bone regeneration space. Below is a detailed introduction to these components:
1. Membrane Tacks
Membrane tacks are primarily used to secure the barrier membrane in place, preventing it from shifting or dislodging during the healing process. They are typically made from biocompatible materials, such as titanium alloy, to ensure long-term presence in the body without causing adverse reactions. Membrane tacks come in various designs, including straight tacks, angled tacks, and extraction tacks, to accommodate different surgical sites and angles.
- Straight Tacks:
These are suitable for anterior tooth regions, featuring a straight handle design that facilitates easy operation, allowing precise placement of the tack in the intended position. - Angled Tacks:
Designed for posterior tooth areas or locations requiring a greater operational angle, these tacks have a curved handle that allows for better access to the surgical site, making tack insertion easier. - Extraction Tacks:
These are used to conveniently remove membrane tacks when the barrier membrane needs to be taken out.
2. Bone Screws (Including Tenting Screws)
Bone screws in GBR also serve a fixation purpose but are more commonly used to secure bone graft materials and the composite of the barrier membrane. They are usually made from high-strength, biocompatible materials such as titanium alloy.
- Bone Tacks (DentalMaster):
Common models include sizes 13 and 15, characterized by a wide tack head that effectively secures the barrier membrane. Their specialized design allows for gentle insertion, and the widened body helps provide additional force and prevent dislodgment. - Tenting Screws:
This type of bone screw is commonly used to create and maintain a stable space in the bone defect area, facilitating the regeneration of bone tissue.
Importance of Membrane Tacks and Bone Screws in GBR
The use of membrane tacks and bone screws during GBR procedures can significantly improve the success rate of the surgery by ensuring stable fixation of the barrier membrane and bone graft materials. This creates an optimal environment for bone tissue regeneration. Additionally, the biocompatibility and design of these fixation devices consider the comfort of the patient and postoperative recovery.
Considerations
In actual surgical procedures, the selection and use of membrane tacks and bone screws should be based on the specific conditions of the patient, the surgical site, and the experience of the surgeon. Postoperatively, patients should follow the dentist’s recommendations for care and follow-up to ensure optimal surgical outcomes and maintain oral health.

Who Needs Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR)
- Patients with bone loss due to long-term tooth loss or gum disease
Long-term tooth loss or severe gum diseases (such as periodontitis) can lead to gradual bone loss in the jaw. Before undergoing dental implants or other restorative treatments, these patients often need GBR to increase bone volume and provide sufficient support. - Patients lacking sufficient bone density for dental implant placement
Insufficient bone density poses a significant challenge in dental implant surgeries. For such patients, GBR can stimulate bone tissue regeneration, increase bone density, and create a stable, healthy environment for implant placement. - Patients requiring bone augmentation before or during dental implant surgery
In some cases, patients may need bone augmentation before or during implant placement. GBR is an effective solution to address this issue, helping patients increase bone volume and improve the success rate of the implant surgery.
Recovery and Postoperative Care
The healing process after GBR surgery usually takes several months, depending on the extent of bone loss, the patient’s overall health, and the success of the surgery. During recovery, patients should follow these recommendations to ensure proper healing and reduce the risk of infection:
- Maintain oral hygiene: Patients should regularly brush, floss, and use mouthwash to keep the surgical area clean.
- Avoid irritation: During the healing period, patients should avoid chewing with the teeth near the surgical area to prevent damage to the newly formed bone tissue.
- Follow medical instructions: Patients should strictly follow their doctor’s instructions on taking antibiotics, painkillers, and other necessary medications, and attend follow-up appointments as scheduled.
- Be mindful of diet: During recovery, patients should opt for soft or liquid foods and avoid hard or irritating foods that could negatively affect the surgical site.
Regular dental check-ups are essential for monitoring bone regeneration progress and preparing for implant placement. X-rays or CT scans allow doctors to evaluate the effectiveness of bone regeneration and adjust the treatment plan if necessary.
Conclusie
Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR) is a crucial surgical procedure in modern dentistry, playing an irreplaceable role in dental implants and periodontal treatments. By skillfully utilizing bone graft materials and barrier membranes, dentists can stimulate and promote the natural bone healing and regeneration process, offering patients a valuable opportunity to restore oral health and extend the longevity of dental restorations.
GBR technology not only helps patients rebuild bone lost due to periodontal disease, trauma, or other causes, but also ensures success in dental implant surgeries. The combined use of advanced membrane and bone graft materials allows GBR to facilitate the regeneration of strong, healthy bone, laying a solid foundation for a lasting and functional smile.
Therefore, if you are considering dental implants and are concerned about bone loss, it’s worth consulting your dental professional to determine if Guided Bone Regeneration is right for you. With GBR technology, you can gain more stable implant support, restoring both the function and aesthetics of your teeth, while improving your overall oral health.