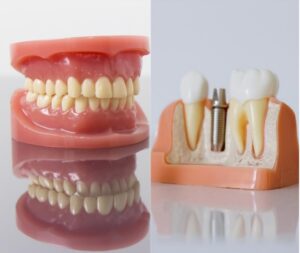
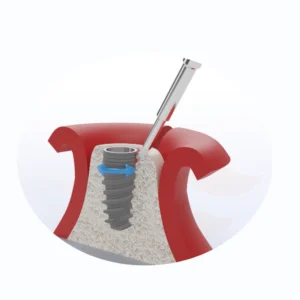
Bone grafting plays a vital role in repairing bone structures and restoring bone function. Bone defects caused by trauma, disease, or surgery often require bone grafting to restore bone integrity and stability. Bone grafting not only promotes bone regeneration and healing but also improves patients’ quality of life by reducing pain and functional impairment caused by bone loss. Therefore, bone grafting holds significant demand and importance in modern medicine.

What is titanium mesh?
Titanium mesh, also known as titanium metal mesh, is a mesh material woven from titanium wires. Titanium is a rare metal characterized by high strength, low density, excellent corrosion resistance, and superior biocompatibility. Titanium mesh is typically manufactured using plain weave, twill weave, or dense weave methods. Depending on its specific application, the specifications and mesh count (the number of holes per inch) vary. The primary material grades for titanium mesh include T1, TA2, GR2, GR3, and R50250, and its surface can either be black (coated with graphite emulsion) or bright (without graphite coating).
Due to its unique physical and chemical properties, titanium mesh has been widely applied across various fields. In the medical field, titanium mesh, with its excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, serves as an ideal material for bone grafting procedures. It not only provides structural support for bone regeneration but also reduces the amount of autologous bone graft needed, lowering surgical risks and complications.
Additionally, titanium mesh offers outstanding plasticity, allowing it to be trimmed and shaped based on a patient’s specific needs to fit various bone defect shapes and sizes. As a result, in cases where bone grafting is necessary for bone volume augmentation during dental implants, titanium mesh has emerged as an ideal choice.
The Principles of Titanium Mesh in Bone Grafting
The principles behind titanium mesh in bone grafting primarily rely on its material properties of high strength, flexibility, and biocompatibility. These characteristics enable titanium mesh to provide stable and long-lasting structural support to bone defect areas, prevent soft tissue collapse, and promote bone tissue growth and repair.
Firstly, the high-strength properties of titanium mesh allow it to deliver stable and durable structural support to bone defect sites. This support is crucial for bone regeneration, as it prevents bone displacement or collapse caused by external forces or physical activity during the healing process. By creating a stable mechanical environment, titanium mesh facilitates the proliferation and differentiation of bone cells, thereby accelerating the bone regeneration process.
Secondly, the flexibility of titanium mesh allows it to adapt to the complex shapes and sizes of bone defects. This adaptability ensures a better fit to the bone defect site during implantation, while also minimizing pressure and damage to surrounding soft tissues. By preventing soft tissue collapse, titanium mesh protects adjacent blood vessels and nerves, creating a more favorable biological environment for bone regeneration.
Finally, the biocompatibility of titanium mesh is one of its key characteristics as a bone grafting material. Biocompatibility means that titanium mesh is well-tolerated by human tissues and does not cause rejection or inflammatory reactions. This compatibility allows titanium mesh to remain in the body for extended periods without adverse effects on health. More importantly, the microstructure and chemical composition of the titanium mesh surface promote the attachment and growth of bone cells, further enhancing bone tissue growth and repair.
Key Advantages of Titanium Mesh in Bone Grafting
Titanium mesh has demonstrated significant advantages as an advanced medical technology in the field of bone defect repair. Below are the primary benefits of titanium mesh in bone grafting:
1. High Plasticity:
Titanium mesh features excellent plasticity, which means it can be flexibly shaped according to the specific needs of the patient to fit bone defects of varying shapes and sizes. This adaptability ensures a precise fit to the defect site, providing targeted support for bone regeneration.
2. Flexible Shaping for Various Bone Defect Areas:
Thanks to its woven structure, titanium mesh can be easily cut, bent, and shaped to match complex bone defect geometry. This flexibility makes titanium mesh an ideal choice for addressing bone defects of different locations and severities, whether flat or irregular areas.
3. Strong Biocompatibility:
Titanium mesh boasts outstanding biocompatibility, meaning it interacts well with human tissues and is unlikely to trigger rejection or inflammatory responses. This biocompatibility reduces the risk of infection and promotes bone cell attachment and growth, thereby accelerating the bone healing process.
4. Reduced infection risk and enhanced bone healing:
Due to its biocompatibility and favorable surface properties, titanium mesh minimizes bacterial colonization and the risk of infection. Simultaneously, it provides an ideal environment for bone cell adhesion and growth, facilitating bone tissue regeneration and repair.
5. Excellent Mechanical Strength:
Titanium mesh offers high strength and durability, delivering stable and long-lasting support to bone defect areas. This mechanical strength ensures that the grafting material remains in place during the healing process, preserving the stability and integrity of the bone structure.
6. Stable Support to Prevent Graft Material Loss:
The robust structure of titanium mesh resists external forces and internal pressures, providing stable support to the defect area. This prevents the grafting material from shifting or being lost, ensuring smooth bone regeneration.
7. Wide Range of Applications:
Titanium mesh has a broad range of applications, including dental implants, craniofacial reconstruction, and bone defect repair. Whether for minor bone defects or extensive skeletal damage, titanium mesh offers effective and reliable solutions.
Clinical Applications of Titanium Mesh in Dentistry
1. Bone Augmentation Surgery
Bone augmentation is a common preparatory procedure in dental implantology, especially for patients with insufficient bone volume. Titanium mesh plays a crucial role in these procedures in the following ways:
- Providing Structural Support: With its high strength and excellent plasticity, titanium mesh offers necessary structural support to deficient bone areas, ensuring implant stability and long-term success.
- Guiding Bone Regeneration: Acting as a barrier membrane, titanium mesh directs bone cells and blood vessels into the defect area, promoting new bone formation. It also prevents soft tissue and other cells from invading, ensuring effective bone regeneration.
- Combining with Bone Grafting Materials: Titanium mesh is often used in conjunction with autogenous bone, allografts, or bone substitute materials to optimize the bone quantity and quality around implants. These materials integrate tightly with new bone tissue through the mesh’s porous structure, further enhancing implant stability.
2. Jawbone Defect Reconstruction
Titanium mesh is an ideal material for repairing jawbone defects caused by trauma, tumor resection, or congenital abnormalities. It offers the following advantages:
- Precision Shaping: Titanium mesh can be custom-designed and shaped to fit the patient’s specific condition, ensuring accurate reconstruction of defect areas.
- Promoting Tissue Regeneration: The porous structure of titanium mesh facilitates the regeneration of surrounding soft and bone tissues, restoring the form and function of the jawbone.
- Reducing Complications: Using titanium mesh for jawbone defect reconstruction reduces the risk of infection, rejection, and other complications, improving surgical success rates and patient satisfaction.
3. Other Application Scenarios
In addition to the primary applications mentioned above, titanium mesh is also used in other dental clinical procedures, such as:
- Sinus Lift Surgery: In maxillary sinus lift procedures, titanium mesh serves as a scaffold to support the sinus floor elevation, providing sufficient bone volume for implants.
- Periodontal Disease Treatment: In cases of bone loss caused by periodontal disease, titanium mesh can guide the regeneration of periodontal tissues, restoring tooth stability.
4. Precautions
Although titanium mesh has extensive clinical applications in dentistry, the following points must be considered during its use:
- Preoperative Evaluation: A comprehensive assessment of the patient’s oral condition is essential to ensure the suitability of titanium mesh for the specific clinical needs.
- Precision in Operation: The implantation of titanium mesh requires meticulous surgical techniques to ensure stability and proper integration with surrounding tissues.
- Postoperative Care: Close monitoring of the patient’s recovery is necessary to promptly address potential complications such as infection or rejection.
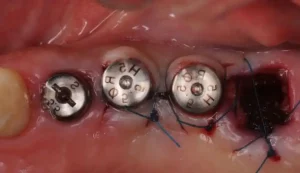
Clinical Success Case of Titanium Mesh Bone Grafting
Titanium Mesh GBR Surgery in Maxillary Anterior Area
How to Select High-Quality Titanium Mesh?
When selecting high-quality titanium mesh, several factors need to be considered to ensure the chosen product meets specific clinical requirements. Below are the key purchasing factors and recommended brands and products:
I. Factors to Consider When Selecting
- Material Purity and Strength
- Purity: The purity of titanium mesh significantly impacts its biocompatibility and mechanical properties. High-purity titanium mesh reduces the risk of rejection and infection while offering superior mechanical performance.
- Strength: The strength of titanium mesh determines its ability to provide stable support to defect areas. High-strength titanium mesh can better resist external forces and internal pressures, ensuring the stability and long-term success of implants.
- Plasticity and Ease of Operation
- Plasticity: The mesh’s plasticity determines its adaptability to various defect shapes and sizes. Easily moldable titanium mesh can fit tightly to defect sites, providing precise support for bone regeneration.
- Ease of Operation: Choose titanium mesh that is easy to cut, bend, and implant. This simplifies the surgical process, reduces operation time, and minimizes patient discomfort.
- Supplier Quality Certification and Technical Support
- Quality Certification: Opt for suppliers with ISO, CE, and other quality management certifications. These certifications ensure the titanium mesh has undergone strict quality control during production.
- Technical Support: Comprehensive technical support, including product consultation, surgical guidance, and after-sales service, ensures that surgeons can receive timely assistance during the procedure.
II. Recommended Brands and Products
DentalMaster
- Product Advantages:
DentalMaster’s titanium mesh is renowned for its high purity, exceptional strength, and excellent plasticity. Each product undergoes rigorous quality control to ensure reliable biocompatibility and mechanical performance. Additionally, DentalMaster provides comprehensive technical support, including product consultation, surgical guidance, and after-sales services, offering convenience and efficiency for clinicians. - Applications:
DentalMaster’s titanium mesh is suitable for bone augmentation procedures in dental implant surgeries, maxillofacial defect reconstruction, and other bone regeneration scenarios. Its outstanding performance and reliable quality make DentalMaster a preferred choice in dental clinical practice. - Website: dentalmastermed.com
FAQs
1. What is the role of titanium mesh in dental bone grafting?
The main role of titanium mesh in dental bone grafting is support and guidance. Due to its high strength, titanium mesh stabilizes the bone graft materials, ensuring their stability in the defect area, preventing soft tissue invasion, and providing space for new bone growth. Its plasticity allows it to be customized according to the shape of the defect, while its porous structure promotes the infiltration of bone cells and blood, further supporting bone regeneration.
2. How long is the recovery time for titanium mesh bone grafting surgery?
The recovery time for titanium mesh bone grafting surgery typically ranges from 4 to 6 months, but this can vary based on individual factors such as the patient’s bone regeneration capacity, the surgical site, and post-operative care. During the recovery period, regular check-ups are necessary to monitor bone tissue growth and rule out any infection risks.
3. Can titanium mesh bone grafting cause rejection reactions?
Titanium mesh is typically made from high-purity titanium, which has excellent biocompatibility. As a result, bone grafting with titanium mesh usually does not cause rejection or allergic reactions. However, like any surgery, there are inherent risks, including infection and bleeding. Therefore, patients should be fully informed about the risks and make decisions under the guidance of their doctor.
4. How can infections be prevented during titanium mesh bone grafting surgery?
To prevent infections during titanium mesh bone grafting surgery, sterile techniques must be followed. This includes sterilizing the operating room, surgical instruments, and ensuring proper hygiene by medical staff. Post-operatively, patients must follow oral care instructions from their doctor, such as using antibacterial mouthwash and maintaining oral hygiene. Regular follow-up visits and taking prescribed antibiotics can further help reduce the risk of infection.
5. What are the advantages of titanium mesh compared to traditional bone graft materials?
- High Mechanical Strength: Titanium mesh has superior mechanical strength, providing stable support for bone graft materials, preventing displacement or collapse, which helps ensure surgical success and promotes recovery.
- Strong Plasticity: Titanium mesh can be customized to fit the shape of the defect, allowing for precise repair. This personalized design improves surgical outcomes and reduces the risk of complications.
- Good Biocompatibility: Titanium mesh has excellent biocompatibility, reducing the risk of rejection and allergies. Its porous surface also facilitates the infiltration of bone cells and blood, promoting bone formation and integration with the graft material.
Conclusion
Titanium mesh is increasingly being used in the field of bone grafting due to its high strength and excellent malleability, making it an essential tool for stabilizing bone defect areas. It prevents soft tissue invasion and provides the necessary space for new bone growth. Additionally, the personalized customization of titanium mesh, its superior biocompatibility, and its ability to simplify surgical procedures enhance surgical precision and reduce the occurrence of complications. The good integration of titanium mesh with surrounding tissues promotes bone defect repair, offering a safer and more reliable treatment solution for patients.
Looking ahead, the application of titanium mesh will become more intelligent and precise. The ongoing development of 3D printing technology will further facilitate the customization of titanium mesh, meeting the needs of more patients. At the same time, the combination of titanium mesh with other bone grafting techniques and regenerative medicine will improve repair outcomes, shorten recovery times, and reduce complications. As technology continues to advance, titanium mesh will provide more advanced and effective treatment solutions for bone defect patients, driving the progress of the bone grafting field.