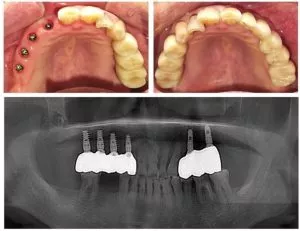
A vital component of contemporary dentistry, dental implants are essential for replacing lost teeth in terms of both appearance and functionality. Selecting the ideal implant may greatly enhance a patient’s quality of life by giving them a look that is similar to that of natural teeth while also ensuring functionality, comfort, and longevity. This article will examine the qualities of a good implant and describe how it satisfies patients’ various demands.
What are dental implants?
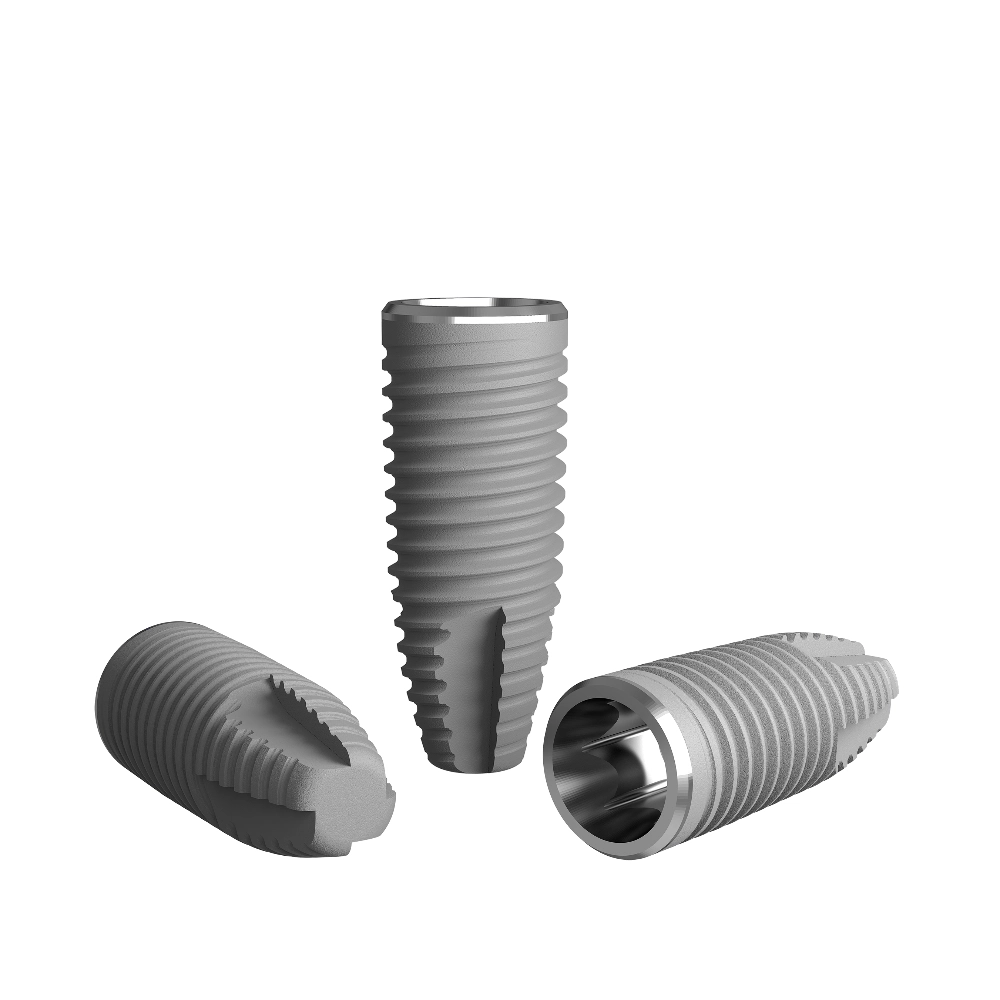
Dental implants are precision-designed artificial tooth root replacements, with the core material typically being highly biocompatible titanium. The choice of this material is not only due to its light weight and strength, but more importantly because titanium can integrate with the human bone, creating stable osseointegration, which provides a solid foundation for the implanted tooth.
The basic components of a dental implant mainly include:
- Implant body: This is the core part of the implant, shaped like a screw, and is implanted into the jawbone to replace the missing natural tooth root. The design of the implant body is carefully considered to ensure a tight integration with the jawbone, forming a solid support structure.
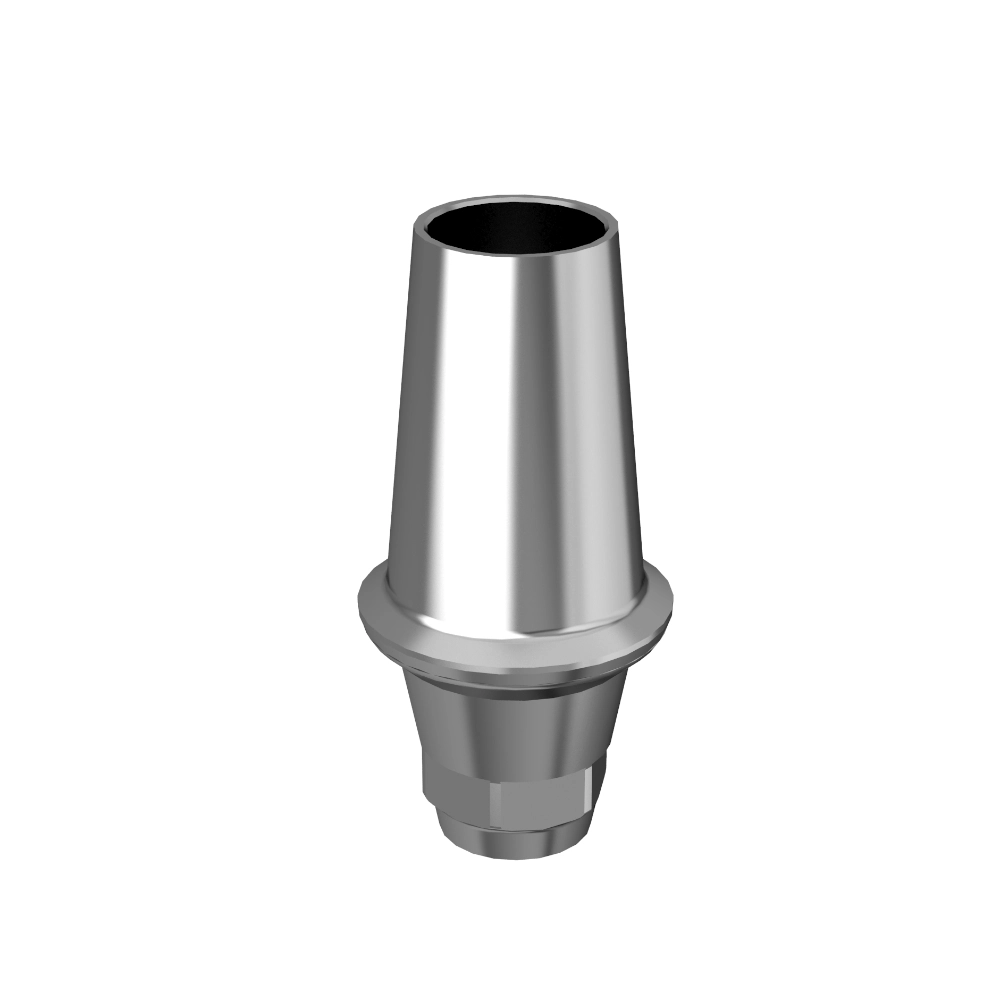
- Abutment: The abutment is placed on top of the implant body and serves as a connector. It is tightly connected to the implant body on one side, while providing a stable platform for the artificial tooth (crown) on the other side. The abutment’s design can be customized to fit the specific needs of the patient.
- Crown: The crown is the final visible part of the implant, which mimics the appearance and function of a natural tooth. The crown is connected to the implant body via the abutment, offering patients a natural, aesthetic, and fully functional tooth replacement option.
The History of Dental Implants
The history of dental implants is a long and exploratory journey. Below are the major stages in its development:
1. Ancient Exploration Stage
Thousands of years ago, humans began exploring dental restoration techniques. Historical records indicate that doctors in Ancient Egypt and India used materials such as ivory and shells to make artificial teeth to replace missing ones. However, these artificial teeth were mostly fixed simply in the mouth without a secure foundation, making it difficult for them to remain in place for a long time.
- Around 2000 BC: The Egyptians made dentures from gold or ivory, connecting them with gold wire to the adjacent healthy teeth, similar to modern bridge crowns.
- Around 1000 BC: The Maya people used materials such as shells and animal teeth to restore teeth, embedding them into the jawbone.
- Around 1100 AD: Arab doctor Alabucasim (or Alabukasim, a Spanish physician) is believed to have first used surgical implant techniques for dental transplantation and replantation. This technique became popular among the European upper classes. Although it was not widely applied at the time, it laid the foundation for later dental implant technology.
2. Modern Attempts Stage
- 1807: Maggiolo used gold to create a root-shaped implant, sparking further exploration of other materials. Though the implant lasted only 14 days, it inspired the use of various materials such as gold, silver, ceramics, and ivory for dental implants.
- 1878: The University of Pennsylvania established its dental school.
- 1891: The heterogeneous dental implant designed by Wrghr received a patent for a one-piece oral implant in the United States.
- 1898: French dentist Pierre Fauchard proposed platinum implants and was granted a patent.
- 1905: American dentist Albrecht Beinfield used titanium alloys to make implants, improving biocompatibility and stability, though still with various issues.
- 1906: Grenield used iridium-platinum and pure gold to make dental implants, with a “fixed abutment” design, earning a patent for the two-piece implant.
- 1909: The term “dental implant” was first used and reported in a British dental journal.
- 1936: With industrial advances, high-strength and corrosion-resistant metals like cobalt-chromium alloys and titanium emerged, leading to improvements in implant design, placement methods, and clinical evaluation.
- 1937: Adms designed a screw-shaped dental implant and spherical attachment abutment.
- 1939: Surock used cobalt-chromium-molybdenum alloys to make a one-piece screw root implant, and Strock proposed that proper occlusion is critical in preventing implant damage and bone resorption, marking the first long-term survival of dental implants in the human body.
3. Modern Development Stage
- 1940s: A two-piece root-shaped dental implant developed by Strock and others at Harvard University achieved long-term clinical success. Animal studies were also conducted to explore the interaction between bone and implants.
- 1940: Boche reported the phenomenon of bone integration with titanium.
- 1943: German inventor Dahl developed button-shaped dental implants, also known as submucosal implants.
- 1946: Goldberg and Gershkof began promoting subperiosteal implants for denture retention.
- 1952: Swedish scientist Brånemark implanted titanium root-shaped artificial teeth into rabbit femurs and discovered bone integration, marking a foundational breakthrough in the use of titanium for dental implants.
- 1963: Sialom reported the use of pin-shaped intrabone implants.
- 1965: Brånemark conducted the first human dental implant surgery on a fully edentulous volunteer. This successful surgery marked the birth of modern dental implant technology. Brånemark continued to refine the technology through extensive research.
- 1966: Brånemark first proposed the theory of “osseointegration.”
- 1967: Gowland and Lewis reported dental implants made from glass-carbon, and Brånemark designed spiral cylindrical implants.
- 1968: Linkow reported leaf-shaped intrabone implants, and Wamer reported screw-type implants.
- 1970: Roberts reported mandibular ramus implants for denture retention.
- 1976: As research on biomaterials advanced, it became clear that single-material implants sometimes failed to meet both biocompatibility and mechanical compatibility requirements. The focus shifted to the design and manufacture of composite materials with predictable performance, aiming to achieve the best bone integration.
- 1977: A conference on implantology was held at the University of Zurich, attended by over 350 renowned international scholars from 15 countries. The theory of “osseointegration” was officially proposed, helping to advance global dental implantology.
- 1978: Dental implants entered the commercial phase, with Brånemark establishing an implant institute at Gothenburg University, marking the clinical application of dental implants. In the same year, the International Academy of Oral Implantology held a conference at Harvard University, discussing the development and methods of dental implants.
- 1979: The Japanese Society of Dental Implantology held a conference, and Leake reported carbon-coated subperiosteal implants.
- 1980: Ches reported aluminum oxide dental implants.
- 1981: Kerley reported mandibular ramus implants; Albrektson and others identified the key factors affecting implant osseointegration.
- 1982: At the Toronto Conference, Brånemark reported extensive research showing bone integration over 15 years, considered a breakthrough in oral medicine and laying the foundation for dental implantology.
- 1985: The International Conference on Oral Implantology was held in Brussels, discussing dental implants and maxillofacial reconstruction.
- 1986: Thomas reported hydroxyapatite-coated titanium implants.
- 1988: The U.S. FDA and the International Institute for Health Research demonstrated the health benefits of dental implants.
- Early 1980s: The first journal dedicated to oral implantology, The International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants, was published, marking the start of good development and academic progress in dental implantology worldwide.
- 1991: Titanium, acid-etched surface treatment spiral implants emerged.
- 1996: The Nobel implant system was renamed.
- 1999: Titanium and hydroxyapatite-coated spiral implants emerged.
- 2000: Titanium, electrochemical oxidation surface-treated spiral implants appeared.
- 2001: Titanium, absorbable spray-sintered medium surface-treated spiral implants emerged.
21st Century:
In the 21st century, digital technology has been widely applied in the field of dental implants. With the use of CT scanning and computer simulations, the position, depth, and angle of implants can be better predicted, improving the precision and success rate of implant surgeries. Additionally, the development of aesthetic restoration techniques has made dental implants look and function more like natural teeth.
The history of dental implants is a symphony of human intelligence and technological advancement. From the initial simple attempts to modern high-precision, personalized implant solutions, every step reflects the tireless effort and relentless pursuit of medical experts and researchers.
What Are the Characteristics of the Best Dental Implants?
what are the best dental implants? Currently, the best dental implants should possess characteristics such as high-quality materials, high biocompatibility, precise manufacturing processes, the use of advanced technology and fine craftsmanship, long-lasting durability and stability, good integration with natural tooth roots, and designs that cater to different needs. These features ensure the long-term stability and aesthetic outcome of the implant, meeting the various demands of patients.
1. High-Quality Materials
- Titanium Alloy and Zirconium Alloy: Titanium alloy is widely used in dental implants due to its excellent biocompatibility, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance. Zirconium alloy (such as titanium-zirconium alloy) provides higher strength while maintaining good biocompatibility, making it suitable for cases with insufficient bone volume or those requiring stronger support.
- Other High-Quality Materials: Pure titanium and bioceramics (such as zirconia) are also top-quality implant materials. Pure titanium offers outstanding biocompatibility and mechanical strength, effectively bonding with bone tissue. Bioceramics are favored by patients for their color and luster, which closely resemble natural teeth, as well as their excellent biocompatibility and resistance to inflammation.
2. High Biocompatibility
- Reduced Rejection Reactions: High-quality implant materials are able to form a good bond with the body’s bone and soft tissues, reducing the occurrence of rejection reactions.
- Promoting Osseointegration: Special treatments on the implant surface (such as hydroxyapatite coatings) further enhance the bond between the implant and bone tissue, accelerating the osseointegration process.
3. Precise Manufacturing Process
- Advanced Processing Technologies: Advanced manufacturing techniques such as casting, machining, heat treatment, electroplating, and coating ensure the precise production of implants.
- Precision in Shape: Using CNC machines and precision machining techniques, implants can be made with accurate shapes and excellent surface treatment.
4. Use of Advanced Technology and Fine Craftsmanship
- Digital Technologies: The use of digital oral scanning, 3D printing, and navigational surgery technologies enhances the accuracy and efficiency of implant procedures.
- Unique Surface Treatment: Through physical or chemical methods, the implant surface is specially treated to improve its hydrophilicity and biocompatibility.
5. Long-Term Durability and Stability
- Ability to Withstand Chewing Forces: High-quality implants have sufficient strength to withstand chewing forces, ensuring the implant’s long-term stability.
- Corrosion Resistance: Implants are resistant to corrosion in the oral environment, extending their service life.
6. Degree of Integration with Natural Tooth Roots
- Osseointegration: The implant forms a strong bond with the jawbone, providing stable support.
- Minimizing Damage: Scientifically designed implants minimize damage to adjacent teeth and periodontal tissues.
7. Designs to Meet Different Needs
- Personalized Design: Implants can be designed based on the patient’s oral structure, bone health, and specific needs.
- Versatility in Applications: Implants are suitable for various situations, including single-tooth replacement, full-mouth, or partial-mouth implants.
Most Popular Dental Implant Brands on the Market
Nobel Biocare
Brand Overview
Nobel Biocare is one of the global leaders in the dental implant industry, known for its outstanding product quality, technological innovations, and extensive clinical experience. The brand is committed to providing efficient and reliable implant solutions to dentists and patients worldwide.
Famous Products and Technologies
Nobel Biocare’s well-known products include the NobelReplace and NobelActive implant series, along with accompanying abutments, restorative components, and more. Its unique surface treatment technologies, such as TiUnite and SLA, significantly enhance the integration of the implant with bone tissue and promote osseointegration.
Why It Is Trusted by Dentists and Patients
With a long history, extensive clinical cases, stringent quality control, and continuous technological innovation, Nobel Biocare has earned the trust of both dentists and patients. Its products excel in long-term stability, aesthetic outcomes, and patient satisfaction.
Straumann
Brand Overview
Straumann is another prestigious dental implant brand, known for its exceptional product design, technological innovation, and high-quality customer service. The brand is dedicated to advancing the field of dental implants and providing high-quality implant solutions to dentists and patients worldwide.
Technological Innovations and Advantages
Straumann’s implant products, such as the ITI hydrophilic implant, feature unique surface treatment technologies that significantly improve the initial stability of implants and speed up osseointegration. The brand also offers a wide range of restorative components and digital solutions to meet the diverse needs of patients.
DentalMaster
Brand Story
DentalMaster, as a dental manufacturing factory, is recognized for its superb craftsmanship and exceptional product performance. The brand offers high-quality implants, as well as OEM customization, with large-scale production capabilities.
Implant Features and Advantages
DentalMaster’s implants are made from advanced titanium alloys, providing excellent biocompatibility and mechanical strength. Its unique surface treatment technology enhances the bond between the implant and bone tissue, while minimizing surgical trauma and recovery time. The brand also offers personalized restoration solutions to meet the aesthetic and functional needs of different patients.
Other Notable Brands
In addition to Nobel Biocare, Straumann, and DentalMaster, there are many other well-known dental implant brands in the market, such as Dentsply Sirona, Zimmer Biomet, and more. These brands are also renowned for their excellent product quality, technological innovation, and extensive clinical experience, offering a variety of implant solutions for dentists and patients worldwide.
In summary, the most popular dental implant brands on the market each have their unique characteristics. They excel in product quality, technological innovation, clinical experience, and customer service. Dentists and patients can choose the most suitable implant brand based on their specific needs and budget.
How to Choose the Right Dental Implant
Evaluation of the Needs of the Patient
Examining the patient’s unique demands in detail is crucial before choosing a dental implant. This entails assessing their practical needs, aesthetic preferences, and oral health. Making decisions based on an understanding of these elements will guarantee that the implant selected satisfies both personal and medical requirements.
Condition of the Oral Health
When choosing an implant, the patient’s dental health is a major consideration. An implant’s success may be impacted by conditions including gum disease, tooth decay, and oral infections. To ascertain if a patient’s dental health is stable enough for an implant, the dentist must do a comprehensive examination.
Density and Volume of Bones
For dental implants to be placed successfully, there must be sufficient bone density and volume. Prior to implant implantation, patients with inadequate bone mass could need further treatments like bone grafting. To guarantee the best stability and osseointegration, the size and type of implant should be determined by the available bone structure.
Aesthetic Standards
The look of the implant is an important consideration for individuals who are worried about the aesthetic result. Particularly for those replacing front teeth or in highly prominent regions, several restoration techniques and implants are designed to more closely resemble natural teeth.
Professional Advice from Dentists
When choosing the ideal implant, the dentist’s training and experience are very important. Based on the patient’s expectations, dental health, and bone quality, they will evaluate each patient’s unique situation and suggest the best implant. A knowledgeable dentist can help the patient make a decision that strikes a balance between cosmetic appeal and long-term success.
The Dentist’s Role in Implant Selection
Dentists assess every pertinent element, including the patient’s general oral health, gum health, and bone structure. They aid the patient in choosing the optimal solution for their long-term dental health and happiness by helping them weigh the benefits and drawbacks of various implant kinds.
Conclusion
The best dental implants combine advanced technology, precision, and high-quality materials. Key features include:
- Quality Materials: High-strength, corrosion-resistant materials like titanium and zirconium, offering good compatibility with surrounding tissues.
- High Biocompatibility: Ensures implants integrate well with the oral environment, reducing the risk of rejection or inflammation.
- Precision Manufacturing: Advanced technology ensures accurate shape, size, and surface characteristics, optimizing fit and functionality.
- Advanced Techniques: Digital scanning, 3D printing, and personalized designs improve precision, reduce recovery time, and enhance outcomes.
- Durability & Stability: Implants are designed to withstand long-term chewing forces and maintain stable attachment to the jawbone.
- Customization: Designs are tailored to individual patient needs, ensuring a perfect fit for both aesthetics and function.
In summary, the best dental implants are durable, stable, biocompatible, and customizable, providing efficient and reliable oral restoration solutions.