Dental implant surgery has undoubtedly brought a revolutionary change for patients with missing teeth, offering a reliable and long-lasting solution. However, not every patient can immediately benefit from dental implants due to challenges like insufficient upper jaw bone volume. In this context, sinus lift surgery has emerged as a critical solution to address this issue.
Sinus lift surgery, also known as sinus augmentation, is an oral surgical procedure aimed at increasing the bone volume between the maxillary sinus and the upper jaw. The primary goal is to enhance the bone quantity and quality, providing a solid foundation for successful dental implant placement. Since the upper jaw often lacks the necessary bone mass and density to support implants, oral surgeons frequently use sinus lift surgery to strengthen the jaw structure.
This blog will delve into sinus lift surgery in dental implant procedures, explaining when it is appropriate to undergo the surgery and its benefits.
What is a sinus lift?
Sinus lift surgery, also known as sinus augmentation, is a surgical procedure specifically designed to address the issue of insufficient jawbone volume for securing dental implants due to bone loss. This procedure involves adding bone material to the space between the molars and premolars, aiming to increase the bone volume in the upper jaw, particularly in the posterior region where the maxillary sinus is located.
The maxillary sinus is an air-filled space situated behind the cheekbone and above the upper teeth. When upper teeth are lost, the bone in this area tends to naturally shrink, making it difficult to support dental implants. Therefore, the primary goal of sinus lift surgery is to create additional bone height and volume in the maxillary sinus area, ensuring the successful placement of dental implants, especially in areas where bone density is typically insufficient, such as around the molars or premolars.
Why is a sinus lift necessary?
The need for sinus lift surgery primarily arises from insufficient height of the maxillary bone or inadequate space between the maxillary sinus and the lower jaw for the placement of dental implants. The main reasons are as follows:
1. Insufficient Maxillary Bone Height
- Anatomical Structure of the Jawbone: The maxillary bone is naturally smaller than the mandibular bone, which means that in some patients, the height of the maxillary bone may not be sufficient to securely support an implant.
- Bone Loss: Some patients experience bone loss due to congenital factors or acquired conditions such as bone resorption after tooth extraction, periodontal disease leading to bone deterioration, or pathological causes such as cysts or tumors that damage the jawbone, further reducing the available volume for implant placement.
2. Insufficient Space Between the Maxillary Sinus and the Lower Jaw
- Maxillary Sinus Expansion: When the upper posterior teeth are lost, the floor of the maxillary sinus may drop down to the position where the missing teeth’s roots were located. This expansion of the sinus reduces the space available for implant placement.
- Small Mandible: Patients with a smaller lower jaw or a relatively larger maxillary sinus may have even more limited space between the maxillary sinus and the mandible, making implant placement difficult.
3. Function of Sinus Lift Surgery
- Increase in Bone Height: Sinus lift surgery works by creating a window in the sinus wall, elevating the bone tissue, and filling the area with materials such as bone grafts (e.g., synthetic bone powder), which increases the bone height at the bottom of the maxillary sinus to provide sufficient support for dental implants.
- Providing a Bone Foundation: The use of bone graft materials provides a strong bone foundation for the sinus lift, ensuring the stability and long-term success of the implants.
4. Suitable Candidates for Sinus Lift Surgery
- Patients with insufficient alveolar ridge height or who have pathological conditions in the maxillary sinus.
- Patients with missing upper posterior teeth and insufficient vertical bone volume in the maxilla.
Two Types of Sinus Lift Surgery
Sinus lift surgery is a procedure designed to increase the bone height at the bottom of the maxillary sinus, with the primary goal of providing sufficient support for subsequent dental implants. This surgery is mainly divided into two types: the Internal Sinus Lift and the External Sinus Lift (Lateral Window). Below is a detailed introduction to these two types of surgeries:
1. Internal Sinus Lift
- Indications: This type is suitable for patients with bone loss ranging from 3mm to 5mm.
- Surgical Steps:
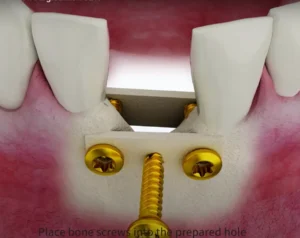
- No additional incisions are needed. The procedure is performed through the implant site.
- The sinus floor is accessed using tapping or ultrasonic bone cutting to remove bone tissue.
- The sinus floor is then elevated, and bone graft material is implanted to increase the alveolar bone height.
- This increases the implantable length for the dental implant.
- Characteristics:
- Less invasive, making it a commonly used method.
- The procedure is relatively simple, with a quicker recovery time.
- Equipment:
2. External Sinus Lift (Lateral Window)
- Indications: This type is suitable for patients with extremely insufficient maxillary bone height, generally less than 2mm.
- Surgical Steps:
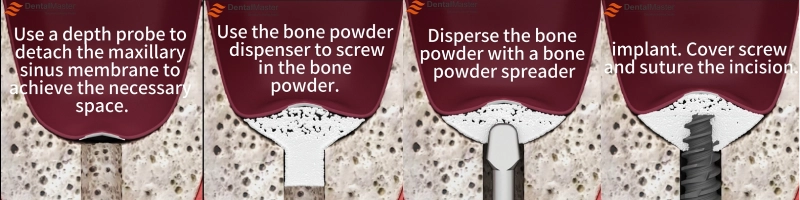
- A window is created in the lateral wall of the maxillary sinus to expose the sinus floor.
- The sinus membrane is separated and pushed upward.
- Bone grafting material is inserted at the window site to increase the bone volume from the sinus floor to the top of the alveolar ridge.
- If sufficient bone volume is achieved, an implant site is directly prepared, and the implant is placed. If bone volume is insufficient, more bone grafting material is added, and dental implants are placed after bone maturation.
- The incision is sutured.
- Characteristics:
- More invasive, typically accompanied by significant swelling and intense pain in the facial region. In severe cases, it may cause infraorbital edema, one-sided headaches, etc.
- Clearer surgical field, allowing the surgeon to have better control over the procedure.
- Higher technical requirements, requiring the surgeon to have extensive clinical experience and strong professional skills.
- Equipment:
Sinus Lift Surgery Complications and Side Effects for Dental Implants
Sinus lift surgery is a procedure used to increase the bone height at the bottom of the maxillary sinus to provide sufficient support for subsequent dental implants. However, the surgery may be accompanied by some complications and side effects. Below is a detailed explanation of the complications and side effects associated with sinus lift surgery for dental implants:
1. Complications
- Infection
- Cause: Insufficient local hygiene control during the surgery, leading to bacteria entering the body.
- Symptoms: Redness and swelling of the oral mucosa, pain, and in severe cases, purulent discharge.
- Management: Use of antibiotics for infection treatment and maintaining oral hygiene.
- Bleeding
- Cause: Damage to surrounding capillaries during surgery.
- Symptoms: Bleeding at the surgical site, possibly accompanied by dizziness and fatigue.
- Management: Hemostasis measures such as compression or hemostatic medications.
- Maxillary Sinus Membrane Perforation
- Cause: Improper technique by the surgeon or underlying issues such as bone osteoporosis in the patient.
- Symptoms: Perforation may lead to the entry of air or other substances into the cranial cavity, potentially causing serious complications such as meningitis.
- Management: Immediate repair of the perforation to prevent further complications.
2. Side Effects
- Pain
- Cause: The surgery causes some irritation to the maxillary sinus.
- Symptoms: Localized pain after the surgery, with varying intensity depending on the patient.
- Management: Ice or wet compresses to relieve pain or use of pain medications.
- Swelling
- Cause: Tissue edema due to surgical trauma.
- Symptoms: Swelling of the facial area, which may affect eating and breathing.
- Management: Physical therapy or medications to reduce swelling.
- Sinusitis
- Cause: Residual bacteria or inflammatory mediators in the maxillary sinus after surgery.
- Symptoms: Nasal congestion, runny nose, headache, and other discomforts.
- Management: Use of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications for treatment.
- Gingivitis
- Cause: Poor oral hygiene after surgery or infection spreading to the periodontal tissues.
- Symptoms: Red, swollen gums, pain, and bleeding.
- Management: Improve oral hygiene, use of antibiotics, and periodontal treatment.
3. Preventive Measures
- Preoperative Preparation
- Conduct a comprehensive oral examination and evaluation to ensure surgical indications.
- Use antibiotics preoperatively to prevent infection.
- Intraoperative Measures
- Choose a qualified and experienced surgeon to ensure proper surgical technique.
- Ensure strict aseptic procedures during surgery to prevent infection.
- Postoperative Care
- Maintain oral hygiene to prevent infections.
- Follow the doctor’s advice, take antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications as prescribed.
- Avoid vigorous exercise and avoid irritating foods to promote wound healing.
In conclusion, sinus lift surgery for dental implants may be associated with some complications and side effects. However, through proper preoperative preparation, correct intraoperative procedures, and postoperative care, these risks can be minimized. Therefore, patients considering sinus lift surgery should fully understand the risks and benefits of the procedure and make decisions under the guidance of a professional dentist.
Does a sinus lift change facial appearance
Sinus lift surgery has minimal direct impact on facial appearance. Any swelling that may occur after the procedure is temporary and gradually subsides as recovery progresses. In the long term, the surgery increases the height of the maxillary bone, providing a stable bone foundation for dental implants, which indirectly improves facial aesthetics.
1. Surgical Process and Facial Impact
- Sinus Lift (Internal) Surgery: This procedure does not require additional incisions. The surgeon uses a tapping method or an ultrasonic bone scalpel to remove bone from the bottom of the maxillary sinus, elevating the sinus floor and filling it with bone graft material. Since the incision is small and performed inside the mouth, the impact on facial appearance is minimal.
- Sinus Lift (External) Surgery: This procedure requires creating a window in the lateral wall of the maxillary sinus to expose the sinus floor, followed by bone grafting and dental implant placement. Although the incision is larger, it is usually well-hidden, and sutures are used, so the direct impact on facial appearance is limited.
2. Postoperative Swelling and Recovery
- Postoperative Swelling: After sinus lift surgery, patients may experience some degree of facial swelling, especially following external sinus lift surgery. This is due to localized tissue edema caused by the surgical trauma. However, this swelling is temporary and typically subsides within a few days to a week after the procedure.
- Recovery Process: As the swelling decreases, the facial appearance gradually returns to its pre-surgical state. During recovery, patients should follow the doctor’s advice, maintain good oral hygiene, and avoid strenuous activities to promote wound healing and reduce swelling.
3. Long-Term Changes in Facial Appearance
In the long run, sinus lift surgery’s impact on facial appearance is primarily reflected in the following ways:
- Increased Maxillary Bone Height: The surgery increases the height of the maxillary sinus floor, providing a stable bone foundation for dental implants. This change occurs internally in the mouth, with minimal direct impact on facial appearance.
- Improved Facial Contours: While the surgery itself does not directly alter facial contours, successful dental implants can restore the function and aesthetics of missing teeth, indirectly improving facial contour.
Postoperative Recovery and Care After Sinus Lift Surgery
Postoperative recovery and care are essential to ensuring the success of the sinus lift surgery and promoting a fast recovery for the patient. Below is a detailed guide on the recovery and care following sinus lift surgery:
1. Postoperative Recovery
- Recovery Time:
Generally, the recovery time after sinus lift surgery may range from 1 to 6 months, depending on individual differences, the complexity of the surgery, and postoperative care.- For mild lift procedures, recovery is relatively quick. Swelling and pain typically decrease within about a week, and the wound generally heals within a month.
- Moderate lift procedures take a bit longer, with swelling and pain alleviating around two weeks, and tissue recovery generally takes about two months.
- Complex lifts take longer to recover, sometimes requiring three months or more to be suitable for dental implant placement.
- Physical Condition:
Different patients have varying physical conditions and recovery capabilities, which can influence the recovery time. Older patients, those with weakened health, or those with other underlying conditions may experience slower recovery, while younger patients with good health may recover more quickly.
2. Postoperative Care
- Medications:
To prevent infection, patients will typically need to take oral medications such as amoxicillin capsules or metronidazole tablets. If the patient is not allergic to penicillin, these two medications are usually preferred.- If there are reactions in the nasal cavity, such as bleeding or lesions, nasal anti-inflammatory medications like nasal drops can be used.
- Dietary Adjustments:
In the first few days after surgery, patients should avoid hard or spicy foods such as nuts or sugarcane to prevent irritation of the wound.- Soft foods and beverages that maintain nutrition, such as fresh juice and vegetable porridge, are recommended.
- Oral Hygiene:
After surgery, use a soft-bristled toothbrush and rinse the mouth with warm saltwater to prevent infection and promote wound healing.- Avoid vigorous rinsing or brushing to prevent irritation of the wound.
- Rest and Activity:
Patients should avoid strenuous exercise and excessive fatigue after surgery, as this can affect the recovery process.- It is important to rest and get plenty of sleep.
- Regular Check-ups:
Follow the doctor’s advice to schedule regular check-ups to assess the recovery progress.- If there are signs of infection during recovery, such as fever, increased pain, or pus, seek medical attention immediately.
- Other Considerations:
- Avoid sneezing post-surgery, as it could affect the implanted bone graft material or membrane in the maxillary sinus. If sneezing is unavoidable, pinch the nose or use a tissue to cover the mouth and nose to reduce the pressure impact on the sinus.
- Avoid blowing the nose to prevent irritation of the sinus.
- Applying local ice packs to the face can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain.
Conclusion
A sinus lift, also known as sinus augmentation, is a surgical procedure designed to increase the bone volume in the upper jaw, particularly in the maxillary sinus area, to support dental implants. It is suitable for patients with insufficient upper jaw bone height due to tooth loss, bone resorption, or anatomical limitations. The procedure is mainly divided into two types: the internal sinus lift (less invasive, suitable for mild bone loss) and the external sinus lift (more invasive, suitable for significant bone deficiency), both requiring bone graft materials to increase bone volume. The recovery time typically ranges from 1 to 6 months, depending on the complexity of the surgery. Although the surgery has minimal impact on facial appearance, the successful placement of dental implants restores tooth function and indirectly improves facial aesthetics. For patients with insufficient upper jaw bone structure needing dental implants, sinus lift surgery is crucial, and with proper care, it can ensure long-term success.